We’ve all been there — a throbbing forehead, a dull ache behind the eyes, or a sharp pain that disrupts your day. Headaches are one of the most common health complaints worldwide, affecting people of all ages and lifestyles. While most headaches aren’t dangerous, they can be frustrating, debilitating, and sometimes a sign of something more serious.
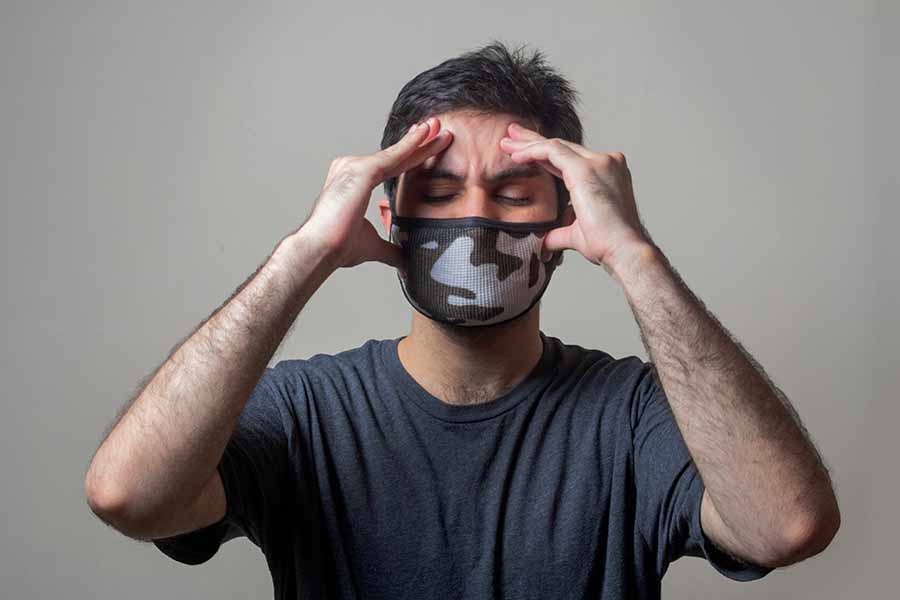

In this post, we break down the different types of headaches, how to treat them, and when it’s time to see a healthcare professional.
Common Types of Headaches
Understanding what kind of headache you’re experiencing is the first step toward effective treatment. Here are the most common types:
1. Tension Headaches
- Description: The most common type. Feels like a constant, dull pressure or tight band around your head, especially at the temples or back of the neck.
- Causes: Stress, poor posture, dehydration, or lack of sleep.
- Treatment: Over-the-counter (OTC) painkillers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, relaxation techniques, massage, and stretching.
2. Migraines
- Description: Intense, throbbing pain often on one side of the head. May be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Causes: Hormonal changes, certain foods or drinks, stress, sleep disturbances, or sensory stimuli.
- Treatment: Prescription medications (like triptans), rest in a dark, quiet room, cold compresses, and preventive medications for chronic cases.
3. Cluster Headaches
- Description: Severe, burning pain around one eye or on one side of the head, often occurring in groups (clusters) over weeks or months.
- Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but linked to abnormal activity in the hypothalamus and often triggered by alcohol or strong smells during a cluster period.
- Treatment: High-flow oxygen, triptan injections, preventive meds, and in some cases, nerve blocks.
4. Sinus Headaches
- Description: Deep, constant pain in the cheekbones, forehead, or bridge of the nose, often accompanied by nasal congestion or a runny nose.
- Causes: Sinus infection or inflammation (sinusitis).
- Treatment: Decongestants, antihistamines, nasal sprays, or antibiotics if caused by infection.
5. Medication Overuse Headaches (Rebound Headaches)
- Description: Frequent headaches caused by overuse of pain relievers.
- Causes: Regular use of OTC or prescription headache medications more than a few days a week.
- Treatment: Gradual withdrawal of the overused medication under medical supervision.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Some headaches can be managed or prevented through simple lifestyle tweaks:
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration is a common headache trigger.
- Maintain a Sleep Schedule: Too much or too little sleep can lead to headaches.
- Manage Stress: Try meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises.
- Watch Your Diet: Avoid trigger foods like processed meats, alcohol, caffeine (in excess), and aged cheeses.
- Limit Screen Time: Take regular breaks from digital devices.
When to See a Specialist
While occasional headaches are normal, some symptoms signal a need for medical attention. See a doctor if you experience:
- Frequent or worsening headaches
- Headaches that wake you up at night
- Headaches after a head injury
- Visual changes, confusion, difficulty speaking, or loss of balance
- A sudden, severe “thunderclap” headache
Headaches that don’t respond to typical treatments
A neurologist or headache specialist can help diagnose and manage complex or chronic headaches, often using imaging tests, blood work, or in-depth evaluations to rule out serious conditions.
Headaches may be common, but they’re not something you have to live with. Identifying the type, tracking your triggers, and knowing when to seek help can make a big difference in your quality of life. If headaches are interfering with your daily activities or causing concern, don’t hesitate to talk to a medical professional — relief is often within reach.